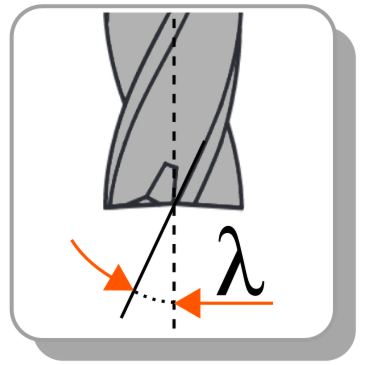
Frez grawerski z węglika spiekanego (HM), kąt wierzchołkowy 60°
Frez do grawerowania napisów z węglika spiekanego (HM). Może być zastosowany do prawie wszystkich materiałów.
Cechy i zalety produktu: wielofunkcyjna konstrukcja narzędzia - kształt V. Kąt wierzchołkowy 60°.
Dostępne średnice [mm]: 3, 4, 5, 6, 8.
Cechy i zalety produktu: wielofunkcyjna konstrukcja narzędzia - kształt V. Kąt wierzchołkowy 60°.
Dostępne średnice [mm]: 3, 4, 5, 6, 8.
| Manufacturer: | EMUGE-FRANKEN |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer Part Number: | 1710 |
| Coating: | no coating |
| Cutting Angle α/σ [°]: | 60 |
| Cutting diameter Ød₁ [mm]: | 3 |
| Cutting Length l₂ [mm]: | 4 |
| Cutting Material: | Solid Carbid (VHM) |
| Cutting Tolerance: | h6 |
| Helix Angle [deg]: | 0 |
| Internal Cooling Supply: | no internal cooling supply |
| Number of Flutes Z: | 1 |
| Overall length l₁ [mm]: | 50 |
| Shank Type: | Straight Shank (DIN 1835-A) |
| Tool Interface Norm: | DIN 6535 |
| P1.1: Cold-extrusion steels, construction steels, free-cutting steels, ≤600 N/mm2 |
| P2.1: Construction steels, case-hardened steels, steel castings, ≤800 N/mm2 |
| P3.1: Case-hardened steels, heat-treatable steels, cold work steels, ≤1000 N/mm2 |
| P4.1: Heat-treatable steels, Cold work steels, Nitriding steels, ≤1200 N/mm2 |
| P5.1: High-alloyed steels, Cold work steels, Hot work steels, ≤1400 N/mm2 |
| M1.1: Ferritic, martensitic, ≤ 950 N/mm2 |
| M2.1:Austenitic, ≤ 950 N/mm2 |
| M3.1: Austenitic-ferritic (Duplex), ≤ 1100 N/mm2 |
| K1.1: Cast iron with lamellar graphite (GJL), 100-250 N/mm2 |
| K1.2: Cast iron with lamellar graphite (GJL), 250-450 N/mm2 |
| K2.1: Cast iron with nodular graphite (GJS), 350-500 N/mm2 |
| K2.2: Cast iron with nodular graphite (GJS), 500-900 N/mm2 |
| K3.1: Cast iron with vermicular graphite (GJV), 300-400 N/mm2 |
| K3.2: Cast iron with vermicular graphite (GJV), 400-500 N/mm2 |
| K4.1: Malleable cast iron (GTMW, GTMB), 250-500 N/mm2 |
| K4.2: Malleable cast iron (GTMW, GTMB), 500-800 N/mm2 |
| N1.2: Wrought aluminium alloys, ≤350 N/mm2 |
| N1.3: Wrought aluminium alloys, ≤550 N/mm2 |
| N1.4: Aluminium cast alloys, Si ≤ 7% N/mm2 |
| N1.5: Aluminium cast alloys,7% < Si ≤ 12% N/mm2 |
| N1.6: Aluminium cast alloys,12% < Si ≤ 17% N/mm2 |
| N2.1: Pure copper, low-alloyed copper, ≤ 400 N/mm2 |
| N2.2: Copper-zinc alloys (brass, long-chipping), ≤ 550 N/mm2 |
| N2.3: Copper-zinc alloys (brass, short-chipping), ≤ 550 N/mm2 |
| N2.4: Copper-aluminium alloys (alu bronze, long-chipping) , ≤ 800 N/mm2 |
| N2.5: Copper-tin alloys (tin bronze, long-chipping), ≤ 700 N/mm2 |
| N2.6: Copper-tin alloys (tin bronze, long-chipping), ≤ 400 N/mm2 |
| N2.7: Special copper alloys, ≤ 600 N/mm2 |
| N3.1: Magnesium wrought alloys, ≤ 500 N/mm2 |
| N3.2: Magnesium cast alloys, ≤ 500 N/mm2 |
| N4.1: Duroplastics (short-chipping) |
| N4.2: Thermoplastics (long-chipping) |
| N5.2: Tungsten-copper alloys |
| S1.1: Pure titanium, ≤ 450 N/mm2 |
| S1.2: Titanium alloys, ≤ 900 N/mm2 |
| S2.1: Pure nickel, ≤ 650 N/mm2 |
| S2.2: Nickel-base alloys, ≤ 1000 N/mm2; |
Write Your Own Review
Featured Product